To set up HAProxy on a Linux server, install the HAProxy package, enable and start the service, then configure a frontend to listen on ports 80/443 and backends pointing to your app servers. Add health checks, SSL termination (optional), logging, and reload the service. Test failover, persistence, and security before going live.
If you’re learning how to setup HAProxy on Linux server, this guide covers installation, configuration, SSL, health checks, logging, tuning, and troubleshooting. With 12+ years managing high-traffic platforms, I’ll walk you through a clean, production-ready path that’s beginner-friendly, secure, and optimized for performance.
What is HAProxy and Why Use it?
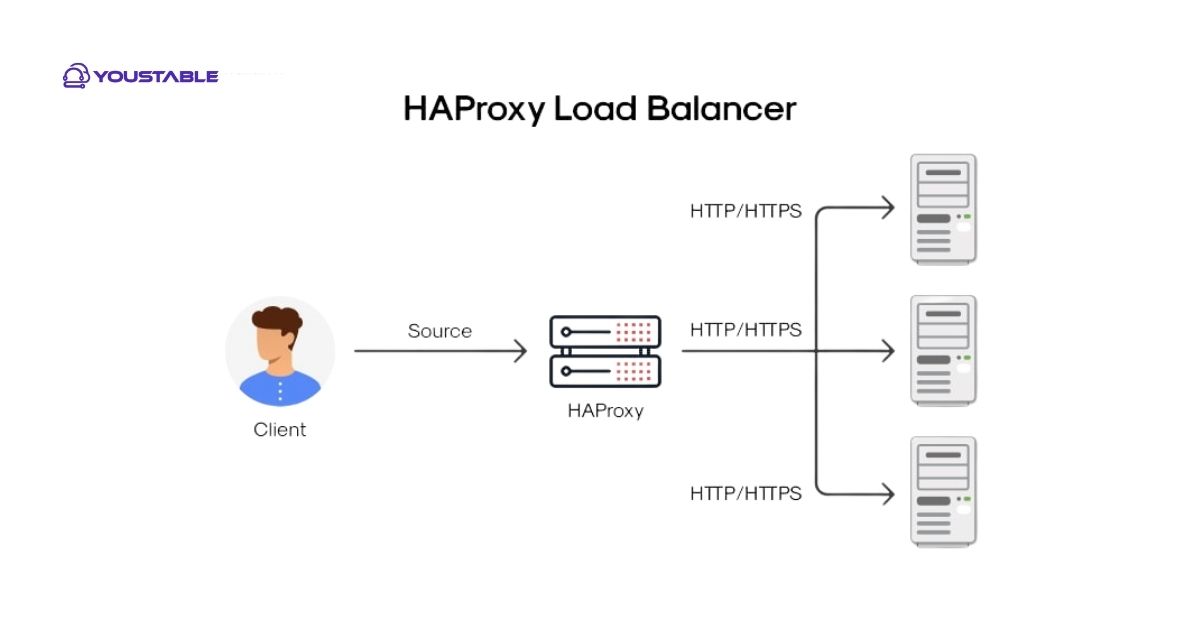
HAProxy (High Availability Proxy) is a fast, reliable open-source TCP/HTTP load balancer and reverse proxy. It sits in front of application servers and efficiently distributes traffic, improves scalability, and increases uptime. It supports health checks, SSL termination, sticky sessions, ACL-based routing, HTTP/2, and advanced observability.
Prerequisites
- Linux server (Ubuntu 22.04/24.04, Debian 12, Rocky/AlmaLinux 9, RHEL 9)
- Root or sudo access
- DNS A/AAAA records pointing to the HAProxy server (e.g., example.com)
- Open firewall ports: 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and SSH
- Two or more backend app servers (Nginx/Apache/Node/etc.)
Step-by-Step: How to Setup HAProxy on Linux Server
1) Install HAProxy
Use your distribution’s package manager. These commands install the latest supported version from official repos.
# Ubuntu / Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y haproxy
# RHEL / Rocky / AlmaLinux (enable EPEL if needed)
sudo dnf install -y haproxy
# Verify version
haproxy -v2) Enable and Start the Service
sudo systemctl enable haproxy
sudo systemctl start haproxy
sudo systemctl status haproxy3) Open Firewall Ports
# UFW (Ubuntu)
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
sudo ufw reload
# firewalld (RHEL/Rocky/AlmaLinux)
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadBasic HAProxy Configuration (HTTP)
Edit the main configuration at /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg. The following minimal setup listens on port 80 and balances traffic to two backend web servers.
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
maxconn 5000
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
timeout connect 5s
timeout client 30s
timeout server 30s
retries 3
frontend http-in
bind *:80
option http-server-close
# Redirect HTTP to HTTPS later if you enable SSL
default_backend web-backend
backend web-backend
balance roundrobin
option httpchk GET /healthz
http-check expect status 200
server web1 10.0.0.10:80 check
server web2 10.0.0.11:80 checkMake sure your app servers answer /healthz with 200 OK. Change IPs to match your environment.
Check Config and Reload
# Validate syntax
sudo haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# Reload without dropping connections
sudo systemctl reload haproxyEnable HTTPS and SSL Termination
Terminating TLS at HAProxy simplifies certificate management and can offload crypto from app servers. Let’s use Let’s Encrypt certificates and present HTTP/2 to clients.
1) Obtain Let’s Encrypt Certificates
Stop HAProxy temporarily if you use the standalone challenge, or use DNS challenge to avoid downtime.
# Install certbot
sudo apt install -y certbot && sudo systemctl stop haproxy
# Or: sudo dnf install -y certbot
# Issue a certificate (HTTP-01)
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d example.com -d www.example.com
# Build a single PEM for HAProxy
sudo mkdir -p /etc/haproxy/certs
sudo bash -c 'cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem \
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem > /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem'
sudo chmod 600 /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem
sudo systemctl start haproxy2) Update HAProxy for HTTPS
frontend http-in
bind *:80
redirect scheme https code 301 if !{ ssl_fc }
default_backend web-backend
frontend https-in
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem alpn h2,http/1.1
option http-server-close
http-response set-header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
default_backend web-backendReload and verify with SSL Labs. Automate renewal by recreating the PEM after each Certbot renewal using a post-hook.
# Automate PEM concat after renewal
echo '#!/bin/sh
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem \
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem > /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem
systemctl reload haproxy' | sudo tee /etc/letsencrypt/renewal-hooks/post/haproxy.sh
sudo chmod +x /etc/letsencrypt/renewal-hooks/post/haproxy.shLoad-Balancing Methods, Health Checks, and Stickiness
Choose a balancing algorithm based on traffic patterns, then confirm health checks work. Add stickiness if your app needs sessions pinned to a server.
- Algorithms:
roundrobin(default),leastconn(busy sites),source(client IP hash) - HTTP health checks:
option httpchk GET /healthzwithhttp-check expect status 200 - Sticky sessions: insert cookies or use IP hash
backend web-backend
balance leastconn
cookie SRV insert indirect nocache
option httpchk GET /healthz
http-check expect status 200
server web1 10.0.0.10:80 check cookie w1
server web2 10.0.0.11:80 check cookie w2Routing with ACLs (Path- and Host-Based)
ACLs let you route traffic to different backends by path or hostname. Great for microservices or blue/green deployments.
backend api-backend
balance roundrobin
server api1 10.0.0.20:8080 check
server api2 10.0.0.21:8080 check
backend static-backend
balance roundrobin
server s1 10.0.0.30:80 check
frontend https-in
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem alpn h2,http/1.1
acl host_api hdr(host) -i api.example.com
acl is_static path_beg -i /assets/ /static/
use_backend api-backend if host_api
use_backend static-backend if is_static
default_backend web-backendLogging and Observability
Enable detailed logs and a stats endpoint to monitor health and performance.
# /etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy.conf
$AddUnixListenSocket /dev/log
$template Haproxy,"%timegenerated% %HOSTNAME% haproxy: %msg%\n"
:programname, startswith, "haproxy" -/var/log/haproxy.log
& stop
# Restart rsyslog
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog# Add to haproxy.cfg (global or defaults section)
stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin
stats timeout 30s
# Add a web stats page (optional)
listen stats
bind *:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 10s
stats auth admin:StrongPass_hereUse tail -f /var/log/haproxy.log and echo "show stat" | socat stdio /run/haproxy/admin.sock for real-time insight.
Performance Tuning and Security Hardening
- Capacity: Raise
maxconninglobaland tune OS limits (nofile,somaxconn). - Keepalives: Use
option http-keep-aliveand sensible timeouts (30–60s client/server). - Transport: Enable HTTP/2, strong ciphers, and HSTS on HTTPS frontends.
- Security: Restrict admin stats, run as non-root, and keep HAProxy updated.
- DDoS/abuse: Rate-limit with stick-tables; block abusive IPs.
global
maxconn 20000
tune.ssl.default-dh-param 2048
defaults
timeout connect 5s
timeout client 60s
timeout server 60s
# Basic rate limiting example
frontend https-in
# ... existing bind/ssl ...
stick-table type ip size 200k expire 30s store gpc0,http_req_rate(10s)
http-request track-sc0 src
acl too_many req_rate(sc0) gt 100
http-request deny if too_manyTroubleshooting Common Errors
- Service won’t start: Run
haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgto validate syntax and check/var/log/haproxy.log. - Port already in use: Another service binds to 80/443. Stop it or change ports.
- 503 Service Unavailable: All backends unhealthy. Verify health endpoint, firewall, and app status.
- SSL errors: Ensure PEM file order (fullchain first, then privkey) and permissions (
600). - SELinux (RHEL): Allow outbound connects if needed:
sudo setsebool -P haproxy_connect_any 1.
High Availability and Production Tips
- Redundancy: Run two HAProxy nodes with VRRP (keepalived) for a floating virtual IP.
- Blue/Green: Use ACLs to shift a small percentage of traffic to the new version, then increase gradually.
- Zero-downtime reloads: Always
systemctl reload haproxyafter config checks. - Observability: Export logs to a SIEM; scrape stats into Prometheus/Grafana.
- Backups: Keep version-controlled configs and secure certificate backups.
Complete Example: Production-Ready haproxy.cfg
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
maxconn 20000
tune.ssl.default-dh-param 2048
stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin
stats timeout 30s
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-keep-alive
timeout connect 5s
timeout client 60s
timeout server 60s
retries 3
frontend http-in
bind *:80
redirect scheme https code 301 if !{ ssl_fc }
default_backend web-backend
frontend https-in
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/haproxy/certs/example.com.pem alpn h2,http/1.1
http-response set-header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
stick-table type ip size 200k expire 30s store gpc0,http_req_rate(10s)
http-request track-sc0 src
acl too_many req_rate(sc0) gt 100
http-request deny if too_many
default_backend web-backend
backend web-backend
balance leastconn
option httpchk GET /healthz
http-check expect status 200
cookie SRV insert indirect nocache
server web1 10.0.0.10:80 check cookie w1
server web2 10.0.0.11:80 check cookie w2
listen stats
bind *:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 10s
stats auth admin:StrongPass_hereYou now have a clear path to deploy, secure, and scale HAProxy on Linux. Follow the steps, validate each change, and consider managed infrastructure from YouStable if you prefer expert-backed reliability from day one.
FAQs: HAProxy on Linux
Is HAProxy a reverse proxy or load balancer?
Both. HAProxy acts as a reverse proxy, terminating client connections and forwarding to backend servers, and as a load balancer distributing requests using algorithms like roundrobin or leastconn. It supports HTTP, TCP, and TLS features for modern application stacks.
Which Linux distro is best for HAProxy?
Ubuntu LTS and Debian are popular for fast setup and frequent security updates. RHEL-based distros (Rocky/AlmaLinux) offer enterprise stability. Choose what aligns with your team’s package ecosystem and support requirements.
How do I enable sticky sessions in HAProxy?
Use cookie-based stickiness in the backend with cookie SRV insert and assign a cookie value to each server. Alternatively, use balance source to hash the client IP. Cookie-based is more reliable for multi-subnet users.
Can HAProxy handle SSL for multiple domains?
Yes. Place multiple PEM files in /etc/haproxy/certs and use crt-dir /etc/haproxy/certs on the bind line. HAProxy will present the correct certificate via SNI based on the requested hostname.
How do I make HAProxy highly available?
Deploy two HAProxy nodes and use keepalived (VRRP) to advertise a floating virtual IP. Both nodes share the same configuration; only the master answers. On failover, the VIP moves to the standby with minimal interruption.