DDR4 vs DDR5 marks a significant evolution in memory technology, driving the next leap in computer performance. As modern systems demand faster data processing, improved multitasking, and better energy efficiency, the type of RAM you choose plays a major role. DDR4 has powered PCs for years, but DDR5 is now taking over with its enhanced speed, bandwidth, and power management features. Understanding the differences helps users make the right upgrade decision for gaming, creative work, or professional use.
In this article, we’ll explore the core differences between DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM, focusing on speed, power efficiency, architecture, and compatibility. You’ll also see a clear performance comparison and learn which memory type suits your computing needs best — whether you’re upgrading your current setup or building a new system from scratch.
What Is DDR RAM and How It Works
DDR, or Double Data Rate memory, is the technology that allows RAM to transfer data twice per clock cycle, improving speed and efficiency. RAM acts as a high-speed bridge between your processor and storage, temporarily holding data that your system needs to access quickly.
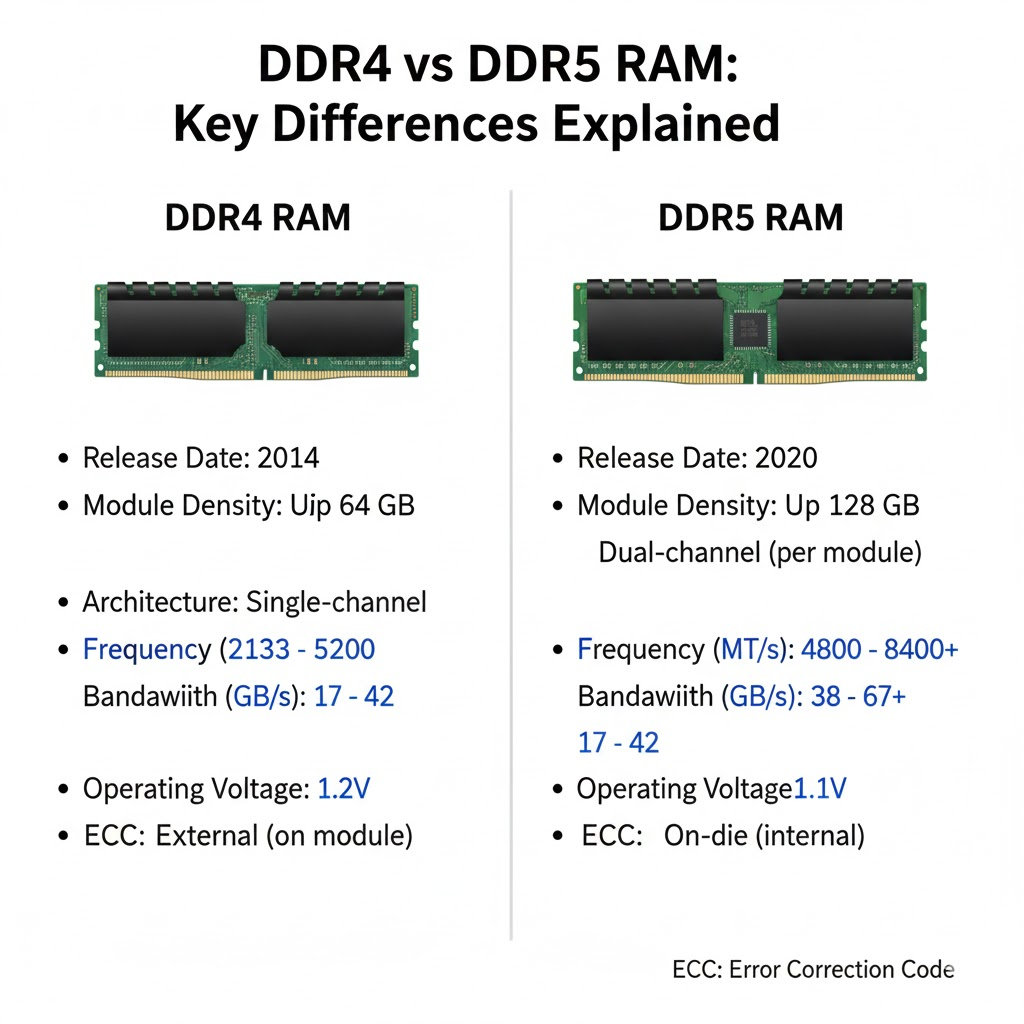
Over the years, DDR technology has evolved from DDR1 to DDR5, with each generation improving transfer rates and reducing power consumption. DDR4 has been the standard for nearly a decade, while DDR5 introduces a new architecture built for multi-core CPUs and bandwidth-heavy applications. This evolution ensures smoother multitasking, faster loading times, and improved stability across all computing environments.
DDR4 vs DDR5 – Key Differences Explained
To understand how DDR4 vs DDR5 differ, let’s look at their technical and practical aspects side by side.
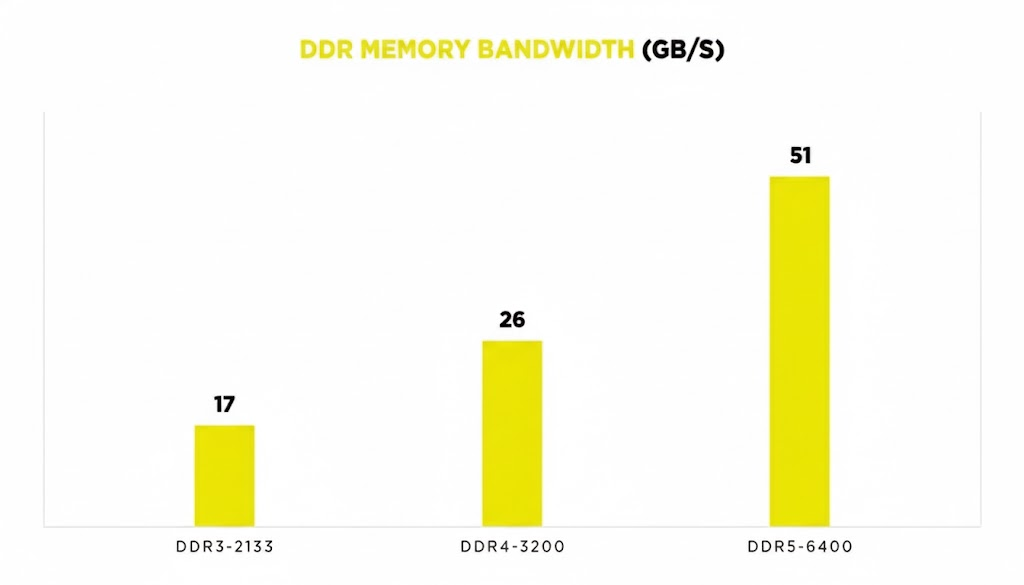
Speed and Bandwidth
One of the biggest differences between DDR4 and DDR5 is speed. DDR4 typically ranges between 2133 MHz and 3200 MHz, while DDR5 starts around 4800 MHz and goes well beyond 8000 MHz on newer modules.
This increased bandwidth means DDR5 can handle more data at once, improving responsiveness in heavy multitasking and gaming. For users working with 3D rendering, virtualization, or high-resolution editing, this translates to smoother performance and shorter processing times.
Latency and Performance
While DDR5 offers higher speeds, its latency (response delay) is slightly higher compared to DDR4. However, the improved bandwidth compensates for this, resulting in better overall system performance.
In real-world scenarios, DDR5’s architecture ensures that the CPU can access memory data faster, enhancing multitasking and heavy computational workloads. Gamers and professionals using performance-intensive software will see a more noticeable benefit over DDR4.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Efficiency is another area where DDR5 improves over DDR4. DDR4 operates at 1.2 volts, while DDR5 reduces this to 1.1 volts. Although this difference seems small, it significantly reduces power draw in systems with multiple memory modules.
This lower voltage helps laptops and servers achieve better battery life and thermal management. Moreover, DDR5 includes a power management IC (PMIC) directly on the module, improving power delivery and stability under load.
Comparison Table: DDR4 vs DDR5
| Feature | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Base Frequency | 2133–3200 MHz | 4800–8400+ MHz |
| Bandwidth | Up to 25.6 GB/s | Up to 67.2 GB/s |
| Voltage | 1.2V | 1.1V |
| Channel Design | Single 64-bit channel | Dual 32-bit channels per module |
| Max Module Capacity | 32 GB | 128 GB+ |
| Power Management | On motherboard | On-DIMM PMIC |
| Error Correction | No | On-die ECC |
| Compatibility | DDR4 motherboards | DDR5 motherboards |
Capacity and Density
When it comes to memory capacity, DDR4 vs DDR5 shows a big leap forward. DDR4 modules generally max out at 32 GB per stick, while DDR5 can reach up to 128 GB or even higher. This massive improvement is due to DDR5’s increased memory density and improved chip design.
For professionals working with virtual machines, data-heavy software, or 4K video editing, higher capacity RAM modules ensure smoother performance and better future-proofing. DDR5 is clearly built to handle the demands of next-generation systems.
Architecture and Channel Design
DDR5 introduces a redesigned architecture to improve efficiency and reliability. Each DDR5 module features dual 32-bit channels instead of DDR4’s single 64-bit channel. This allows for more efficient data flow and reduced bottlenecks, even when performing multiple operations simultaneously.
Additionally, DDR5 includes on-die ECC (Error Correction Code), which helps automatically detect and correct minor data errors, enhancing stability. This architectural refinement makes DDR5 especially beneficial for servers, workstations, and systems requiring continuous uptime and precision.
Compatibility and Upgradability
Compatibility is one area where users need to be cautious. DDR4 and DDR5 are not interchangeable, as they use different pin layouts, voltage requirements, and physical notches.
You cannot install DDR5 RAM on a DDR4 motherboard or vice versa. Therefore, upgrading to DDR5 requires a compatible motherboard and CPU that supports it. Builders planning new systems should check chipset specifications before purchasing RAM to avoid compatibility issues.
DDR4 vs DDR5 – Real-World Performance
In real-world applications, the DDR4 vs DDR5 performance difference depends on the task. For everyday computing, DDR4 still performs admirably and offers better value. However, in CPU-intensive workloads like 3D rendering, AI training, and 4K gaming, DDR5 demonstrates noticeable gains thanks to higher data throughput and efficiency.
Benchmark results show DDR5 delivering smoother multitasking and faster load times. As software continues to evolve to utilize its full potential, DDR5’s performance advantage will become even more significant.
Should You Upgrade to DDR5?
Whether you should upgrade depends on your current system and performance goals. If you’re building a new PC with a modern CPU, opting for DDR5 makes sense due to better speed, scalability, and future-proofing.
However, for users with existing DDR4 setups, the real-world gains might not justify the cost of a full upgrade yet. DDR4 remains a cost-effective choice with plenty of power for gaming and productivity. As DDR5 prices continue to drop, the shift will become more practical for everyone.
Conclusion
The DDR4 vs DDR5 comparison highlights the evolution of memory technology toward higher performance and efficiency. DDR5 offers faster speeds, improved architecture, and better power management — all essential for next-generation computing.
Still, DDR4 continues to deliver solid value for most users, especially when budget and compatibility are key considerations. Ultimately, your choice depends on your system’s needs, workload type, and long-term upgrade plans. DDR5 is the future, but DDR4 isn’t obsolete just yet.