LiteSpeed vs Apache vs Nginx is a critical discussion for hosting providers and system administrators aiming to optimize server performance. Choosing the right web server directly affects page load speeds, scalability, and resource usage. Each server handles requests differently, making some better suited for high-traffic websites while others excel in compatibility or flexibility. Understanding these differences ensures efficient hosting setups, reduces server load, and enhances user experience, ultimately impacting SEO rankings.
This article explores the architecture, performance characteristics, and use cases of LiteSpeed, Apache, and Nginx. You will learn how each server performs under various workloads, understand benchmark results, and gain practical guidance to select the optimal web server for your hosting environment.
What Is a Web Server?
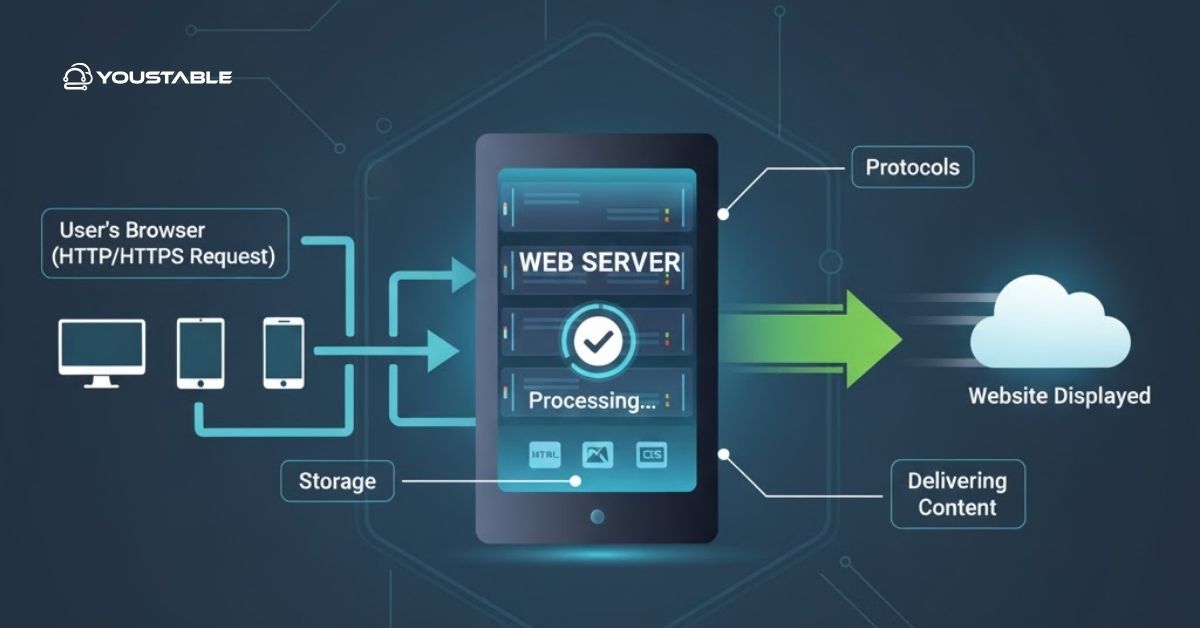
A web server processes client requests and delivers website content over HTTP or HTTPS. When a visitor accesses your site, the server interprets the request, retrieves the relevant data, and returns HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or media files to the browser.
Web servers manage static content, like images and HTML, efficiently, while dynamic content, such as PHP or Python-generated pages, requires additional processing. Performance depends on how the server handles concurrent requests and resource allocation.
Caching plays a significant role in improving response times by storing frequently accessed data. SSL/TLS integration ensures secure connections without compromising speed, a crucial factor for modern web hosting.
Server performance impacts both SEO and user experience. Faster loading times reduce bounce rates and improve search rankings, while inefficient servers can hinder scalability and increase operational costs.
Understanding the capabilities of different web servers allows you to optimize infrastructure and deliver a seamless browsing experience.
Overview of Web Servers
Each web server differs in architecture, caching mechanisms, and performance under load. Evaluating them helps you identify which server aligns with your hosting requirements, workload, and technical expertise.
LiteSpeed
LiteSpeed uses an event-driven architecture to efficiently handle concurrent requests. LSCache integration and HTTP/3 support enable faster page loads and lower latency, especially for dynamic content. Its compatibility with Apache configurations allows easy migration while maintaining performance benefits.
LiteSpeed excels in high-traffic environments by reducing CPU and RAM usage. Licensing fees apply, but the performance gains often justify the cost. Hosting providers seeking fast, scalable, and secure solutions frequently choose LiteSpeed for its speed, built-in caching, and optimized SSL handling.
LiteSpeed Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Very fast performance | Paid license required |
| Built-in LSCache | Smaller community than Apache/Nginx |
| HTTP/3 support | Some plugins may need adjustments |
| Low resource usage | Limited default modules |
Apache
Apache uses a process- or thread-based model, supporting .htaccess files and modular extensions. This flexibility allows detailed customization and easy integration with various applications, making it popular for legacy systems.
Apache is stable, widely supported, and capable of handling high concurrency with proper tuning. It performs well with dynamic content using modules like mod_php, but resource usage tends to be higher under load. Its ease of configuration makes it suitable for administrators familiar with traditional hosting setups.
Apache Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Widely supported | Higher resource usage under load |
| Easy to configure | Slower than LiteSpeed/Nginx for static content |
| Highly modular | Less efficient with high concurrency |
| Flexible .htaccess support |
Nginx
Nginx operates asynchronously with an event-driven design, efficiently handling thousands of concurrent connections. It excels as a reverse proxy and load balancer, reducing server strain and improving scalability.
Nginx is highly efficient in serving static content and managing dynamic requests through FastCGI. Its lightweight footprint and scalability make it ideal for high-performance web applications, microservices, and environments requiring robust reverse proxy capabilities, though configuration may be more complex for beginners.
Nginx Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High concurrency handling | Configuration can be complex |
| Lightweight & efficient | Fewer native modules |
| Excellent reverse proxy | Learning curve for beginners |
| Fast static content delivery |
Also, Read | HAProxy vs Traefik vs Envoy: Open-Source Load Balancer Comparing
LiteSpeed vs Apache vs Nginx: Performance Benchmark Comparison
| Feature / Metric | LiteSpeed | Apache | Nginx |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Event-driven | Process/thread-based | Event-driven, asynchronous |
| Static Content Speed | Fastest (native cache) | Moderate | Very fast |
| Dynamic Content Handling | Excellent (LSAPI) | Good (mod_php) | Good (FastCGI) |
| Resource Usage (RAM/CPU) | Low to moderate | High under load | Low |
| HTTP/3 & QUIC Support | Native support | Via modules | Partial support |
| Caching System | Built-in LSCache | External modules | FastCGI or proxy cache |
| SSL/TLS Performance | Optimized (native handling) | Standard | Efficient |
| Reverse Proxy Support | Yes | Limited | Excellent |
| Configuration Complexity | Moderate | Easy (familiar) | Complex for beginners |
| Best For | High-performance hosting | Legacy or general hosting | Scalable web applications |
Which Web Server Should You Choose?
Choosing a web server depends on workload, environment, and technical expertise. LiteSpeed is ideal for high-traffic websites and dynamic content-heavy platforms, offering speed, caching, and HTTP/3 benefits. Apache works well for general-purpose or legacy hosting where compatibility and ease of configuration are priorities. Nginx excels in scalable environments requiring high concurrency, low resource usage, and robust reverse proxy capabilities.
Consider testing each server with representative workloads before making a final decision. Benchmarks help evaluate response times, resource usage, and caching performance under realistic traffic. Each server has unique strengths: LiteSpeed for speed, Apache for flexibility, and Nginx for scalability. Your choice should balance performance requirements, infrastructure costs, and operational complexity.
Experiment with configurations, optimize caching, and monitor performance regularly to ensure a consistent user experience and server efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding LiteSpeed vs Apache vs Nginx equips you to make informed decisions for your hosting environment. LiteSpeed delivers superior speed and efficiency for high-traffic sites, Apache offers flexibility and broad compatibility, and Nginx provides exceptional scalability for modern web applications. Benchmarking each server under realistic workloads ensures optimal performance, resource utilization, and user experience. Evaluating caching, SSL handling, and reverse proxy capabilities helps you match server strengths with project needs. By choosing the right web server, you enhance site speed, reliability, and SEO rankings, ensuring a professional and high-performance hosting setup.


