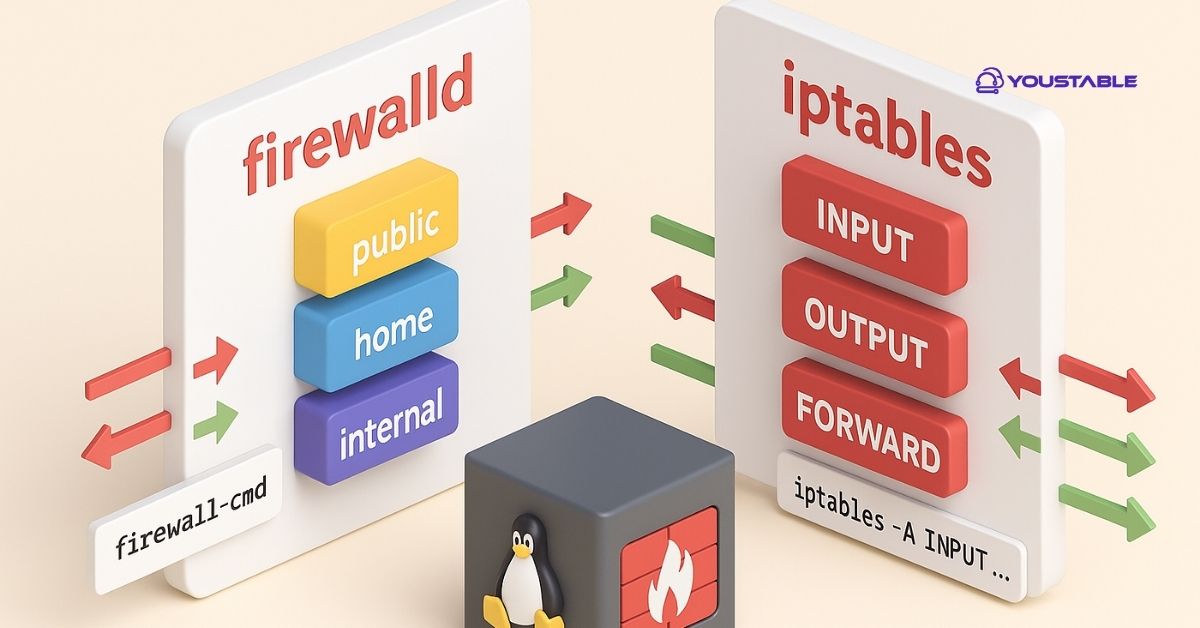
Use FirewallD on a Linux server to manage your firewall with ease and flexibility. FirewallD provides a dynamic way to control network traffic using zones and services, making it simple to secure your Linux server without complicated configurations.
This guide will show you how to use FirewallD on a Linux server—from installation and basic setup to configuring rules and managing firewall services.
Prerequisites
- A Linux server running CentOS, Red Hat, Fedora, or other supported distributions that use FirewallD
- Root or sudo access to install and configure firewall settings
- Terminal access to run commands
Steps to Use FirewallD on a Linux Server
FirewallD is a dynamic firewall management tool that provides a user-friendly way to configure and manage firewall rules on Linux systems. Unlike traditional static firewall tools, FirewallD supports real-time updates without restarting the service, making it ideal for production environments. With zone-based rule organization and support for both IPv4 and IPv6, FirewallD helps secure your server by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined or custom policies.
Step 1: Install FirewallD on the Linux Server
Many modern Linux distributions have FirewallD installed by default. To check and install if necessary:
- Check if FirewallD is installed:
firewall-cmd --version- Install FirewallD if missing:
On CentOS/Red Hat/Fedora:
sudo yum install firewalldOn Ubuntu/Debian (recent versions support it, but may require installing):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install firewalldStep 2: Start and Enable FirewallD Service
Make sure the FirewallD service is running and enabled on boot:
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
sudo systemctl status firewalldActive (running) status means FirewallD is ready to manage your firewall.
Step 3: Basic Use of FirewallD on Linux Server
Once FirewallD is installed and running, you can start using its core functions to manage network traffic. Basic tasks include checking the default zone, adding or removing services and ports, and reloading rules without interrupting network connections. These commands help establish a secure yet flexible firewall setup.
- Check Default Zone
Zones define the trust level of network connections. See your default zone:
sudo firewall-cmd --get-default-zone- List All Zones and Their Settings
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all-zones- Check Services Allowed in Default Zone
sudo firewall-cmd --list-servicesStep 4: Add and Remove Services or Ports
To use FirewallD on a Linux server effectively, you will open or close ports and enable services as needed.
- Add a service (e.g., HTTP):
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent- Remove a service:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-service=http --permanent- Add a port (e.g., TCP port 8080):
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent- Remove a port:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8080/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8080/tcp --permanent- Reload the firewall to apply permanent changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadStep 5: Managing FirewallD on Linux Server
- List all enabled services and ports in the default zone:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all- Get info on a particular zone:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all- Lockdown (panic) mode: Temporarily block all incoming connections except SSH:
sudo firewall-cmd --panic-on- Disable panic mode:
sudo firewall-cmd --panic-offStep 6: Using Rich Rules (Advanced Use)
Rich rules allow more complex firewall policies, such as IP filtering or logging.
- Example: Allow SSH from a specific IP only:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-rich-rule='rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.1.100" service name="ssh" accept'
sudo firewall-cmd --reload- List all rich rules:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-rich-rulesConclusion
To use FirewallD on a Linux server effectively, install and enable the FirewallD service, understand zones, and configure services and ports to control traffic dynamically. FirewallD simplifies managing firewall rules with powerful yet user-friendly commands, enhancing your Linux server’s security while maintaining flexibility. For more detailed usage and advanced rules, explore the official FirewallD documentation, which covers all aspects comprehensively.